Background
The WHO declared the current Monkeypox outbreak a public health emergency of international concern. PCR test is the preferred diagnostic assay. External Quality Assessment Programs (EQAP) provide an independent assessment of the effectiveness of analytical systems, especially with emerging pathogens. There are a few references about EQAP for monkeypox.
Aim
Here, we report the results of the first monkeypox EQAP conducted by a Brazilian EQAP provider, which follows the criteria of ABNT NBR ISO/IEC 17043:2011.
Methods
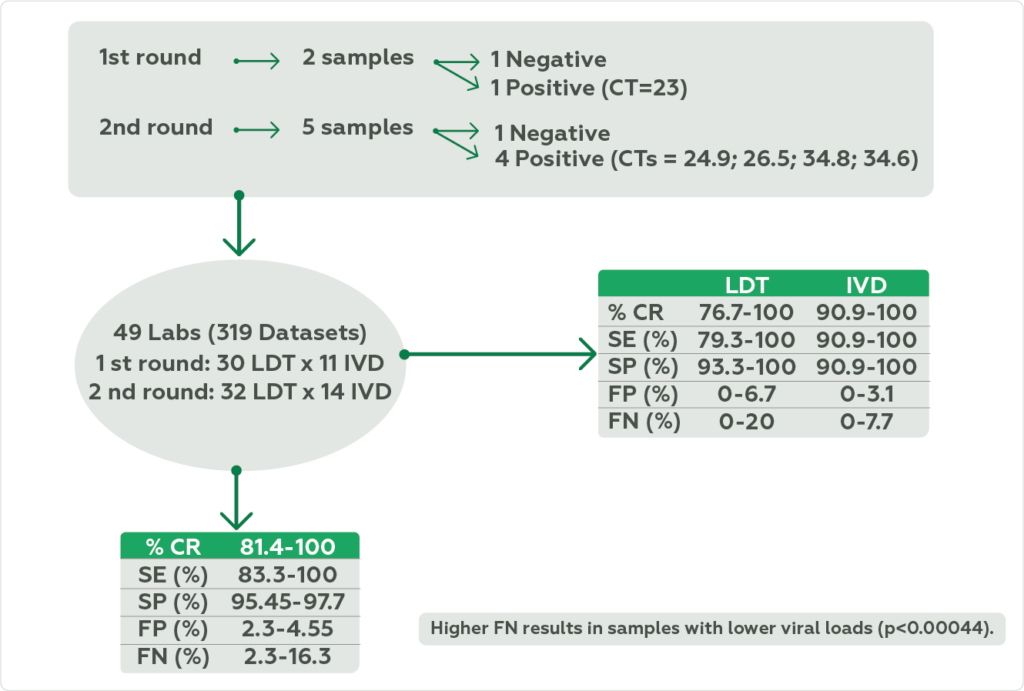
The quality control samples were inactivated lyophilized suspension of Vero cells (BCRJ 0245/ATCC CCL-81) infected with viable monkeypox virus particles and cultured under BSL-3 conditions. The EQAP surveys were conducted in September and October/2022. In the first round, two samples were sent – one negative and one positive cycle threshold (CT) of 23. In the second round, 5 samples with different viral loads were sent (CT of: negative/24.9/26.5/34.8/34.6). The percentage of correct results, sensitivity, specificity, false positive, and false negative were calculated for each sample, and the performance of laboratory-developed test or in vitro diagnosis was compared.
Results
A total of 49 laboratories (38 from Brazil) submitted 319 datasets with qualitative results. In the first round, 30 laboratories used laboratory-developed test methods and 11 laboratories used in vitro diagnosis methods; In the second round, the number of laboratories was 32 and 14, respectively. The percentage of correct results ranged from 81.4-100%, sensitivity from 83.3-100%, specificity from 95.45-97.7%, false positive from 2.3-4.55%, and false negative from 2.3-16.3%. Samples with higher false negative have lower viral loads (p=0.00044) (Figure 1).
The overall percentage of correct results, sensitivity, specificity, false positive, and false negative for laboratory-developed test methods were 76.7-100%, 79.3-100%, 93.3-100%, 0-6.7%, and 0-20%, and for in vitro diagnosis methods were, 90.9-100%, 90.9-100%, 90.9-100%, 0-3.1%, and 0-7.7%, respectively. No statistical difference was found between methods regarding these parameters (Figure 1).
Conclusion
This is the first report of EQAP of monkeypox molecular testing from Brazil. The EQAP showed that monkeypox PCR had an overall good accuracy and performance. False negative rates ranged from 2.3% to 16.3%, suggesting there is room for assay improvement, especially with samples with low viral loads. Laboratory-developed and in vitro diagnosis tests presented similar performance.
Disclosure
The authors confirm that they don’t have any conflict of interest to declare.
Bibliographic References
Petersen E, Kantele A, Koopmans M, Asogun D, Yinka-Ogunleye A, Ihekweazu C, Zumla A. Human Monkeypox: Epidemiologic and Clinical Characteristics, Diagnosis, and Prevention. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2019 Dec;33(4):1027-1043. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2019.03.001. Epub 2019 Apr 11. PMID: 30981594; PMCID: PMC9533922.
Kumar N, Acharya A, Gendelman HE, Byrareddy SN. The 2022 outbreak and the pathobiology of the monkeypox virus. J Autoimmun. 2022 Jul;131:102855. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102855. Epub 2022 Jun 25. PMID: 35760647; PMCID: PMC9534147.
