Introduction - Aim
HPV detection is a global health priority. High-risk HPV (HR-HPV) is one of the primary causes of cervical cancer, while low-risk HPV (LR-HPV) is associated with benign lesions, such as genital warts. Reliable HPV testing requires standardized laboratory performance, and External Quality Assessment (EQA) Programs play a vital role in ensuring accuracy and harmonization. This study compared laboratory performance in an EQA program for the molecular detection of HR-HPV and LR-HPV by PCR/qPCR, organized by a provider accredited according to ABNT NBR ISO/IEC 17043:2011.
Methods
Liquid samples from cervical brushing or cell lysate were utilized in the EQAP. Between 2020 and 2024, laboratories received two quarterly samples to evaluate accuracy (AC), sensitivity (SE), and specificity (SP). These performance metrics were assessed and compared between the High-risk and Low-risk HPV PCR/qPCR using chi-square tests and odds ratios. HR-HPV and LR-HPV AC trends over time were analyzed using the Mann-Kendall test.
Results
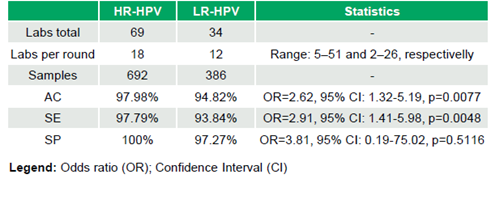
69 laboratories (median 18 laboratories/round, range 5–51; 692 datasets) participated in the HR-HPV evaluation, and 34 laboratories (median 12 laboratories/round, range 2–26; 386 datasets) in the LR-HPV evaluation. HR-HPV results were 97.98% (678/692) AC, 97.79% (620/634) SE, and 100% (58/58) SP, while LR-HPV achieved 94.82% (366/386) AC, 93.84% (259/276) SE, and 97.27% (107/110) SP. Significant differences in SE (OR=2.91, 95% CI: 1.41–5.98, p=0.0048) and AC (OR=2.62, 95% CI: 1.32–5.19, p=0.0077) favored HR-HPV, while SP was comparable (OR=3.81, 95% CI: 0.19–75.02, p=0.5116) (Table 1). No significant trends in AC were observed over time for High-risk HPV testing (τ=-0.046, p=0.795) or Low-risk HPV testing (τ=0.3, p=0.098).
Conclusions
Both evaluations demonstrated strong performance, with HR-HPV showing better sensitivity and accuracy, while specificity was similar. No significant trends in accuracy were observed over time, indicating stability with no changes over time. Detecting LR-HPV remains crucial for managing lesions, enabling cost-effective treatment, reducing transmission, and supporting public health strategies. This study highlights that LR-HPV PCR/qPCR assays have room for improvement to meet HR-HPV standards, emphasizing the need for ongoing refinement and quality assessments.
References
WHO guideline for screening and treatment of cervical pre-cancer lesions for cervical cancer prevention, second edition:Use of mRNA tests for human papillomavirus (HPV)-World Health Organization 2021.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) to screen for cervical pre-cancer lesions and prevent cervical cancer: policy brief-World Health Organization 2022.
Okada PA, Mitrat S, Rojanawiwat A. External quality assessment program for human papillomaviruses DNA testing in Thailand. Pract Lab Med. 2023 Dec 26; 38: e00352. doi: 10.1016/j.plabm. 2023. e00352. PMID: 38292923; PMCID: PMC10825476.