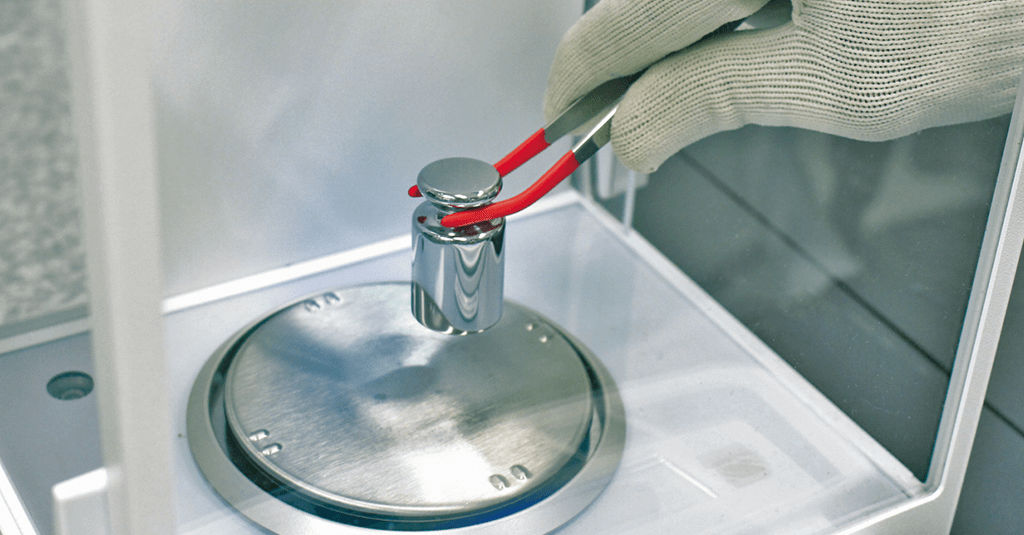
When calibrating, the user reduces costs, fulfills certification and accreditation requirements and ensures quality in the analytical process
Instrument Calibration is a process that certifies that the measurement obtained by an instrument is compatible with what is expected and that it is suitable for use, in order to avoid deviations in the analysis processes and reduce costs.
In general, it consists of comparing the results obtained by the instruments with those obtained by standards (traceable to national/international reference standards), under pre-established and controlled conditions.
In a laboratory, all measuring instruments that have an influence on the accuracy or validity of tests need to be calibrated. In general, also in industries and other segments, calibration must be used in order to avoid changing properties with impacts on products or services.
By performing the Calibration, the user certifies that the instruments used in the analytical process are compatible with the expected performance. Its main benefits are:
- Ensure quality in analytical processes;
- Reduce analytical costs and increase productivity;
- Comply with certification and accreditation requirements;
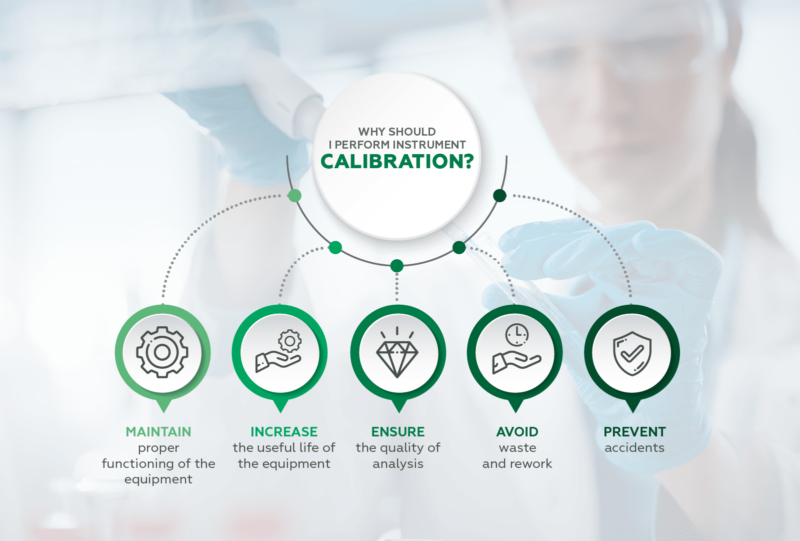
- Maintain proper functioning of instruments;
- Increase the useful life of equipment.
Calibrating avoids waste and rework, as well as preventing accidents. Remember that the instrument must be calibrated after purchase, or before starting use, before and after maintenance. And of course, at stipulated intervals.
Understand calibration in practice
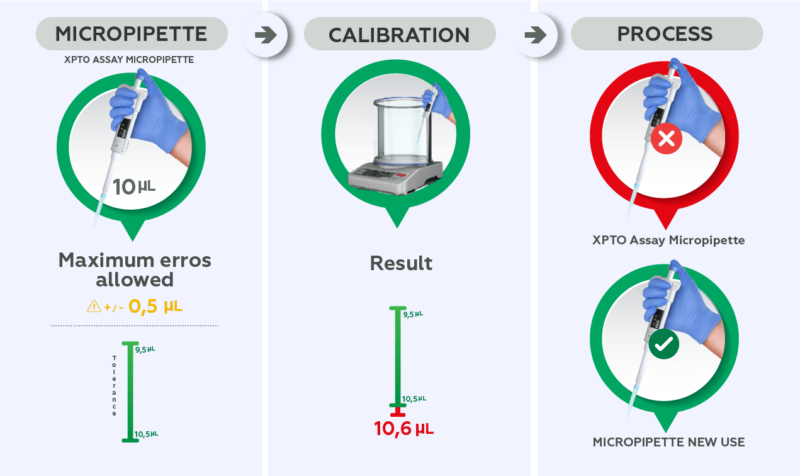
In summary, the purpose of calibration is to verify if the measurement obtained by an equipment is compatible with what is expected and if it is suitable for the activity for which it is intended.
For example: a 10 uL micropipette is used during an assay where the maximum error allowed by the customer is +/- 0.5 uL (tolerance of 9.5 uL to 10.5 uL) and the calibration result shows an average result of 10.6 uL. This instrument should be considered unsuitable for this use and intended for an activity with greater tolerance, if maintenance for adjustments is not performed.
Certification and accreditation in the laboratory segment
The quality in the processes is no longer just an addition, becoming a mandatory item. Some criteria and standards are essential for the proper functioning of the laboratory. Criteria stipulated by CLSI/NCCLS, American Society for Microbiology, ABNT NBR ISO 9001, 15189 and 17034 standards and ABNT NBR ISO/IEC 17025 and 17043 standards, require the calibration of glassware, micropipettes, scales, thermometers, among others.
By contribution to the reliability of results and reduces the costs inherent to testing errors, calibration is now a requirement for certification and accreditation processes.
Ensuring the reliability and credibility of the results is being ahead, it is becoming a natural option. Quality is a determining market differential, especially when these results interfere with health and the environment, which is the case with clinical trials, on food and water, among others.
Why calibrate with Controllab?
Controllab has been accredited by the Coordenação-Geral de Acreditação do Inmetro,under CAL nº 0214, since 2002.
In addition to all the accumulated competence, the delivery time is minimal, ensuring the necessary agility for the instruments to return to the users’ routine without major interruptions, with an excellent cost/benefit ratio.
An extensive scope of instruments is contemplated in the Controllab Calibration Laboratory:
- Scale
- Volumetric flask
- Thermostatic bath
- Burette (glass)
- Thermal chamber (e.g. oven, freezer, refrigerator)
- Conductivimeter
- Volume dispenser
- Analog and digital pressure gauge
- Micropipettes
- pH meter
- Pyconometer
- Pipette (glass)
- Beaker
- Glass and digital thermometer
- Titrator
- Analog and digital vacuum gauge
When calibrating, the following benefits are built into your process:
Realize a calibração do seu instrumento/equipamento acessando o catálogo da Controllab.



