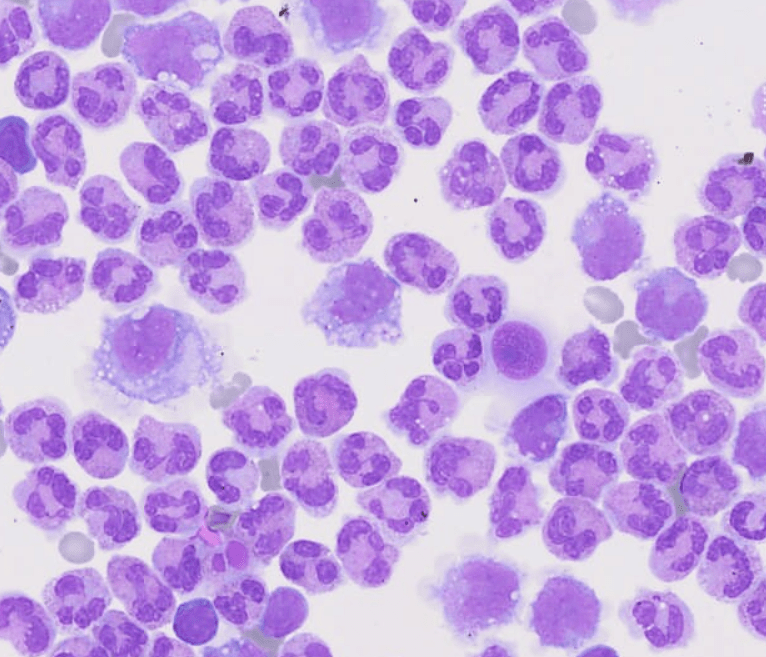
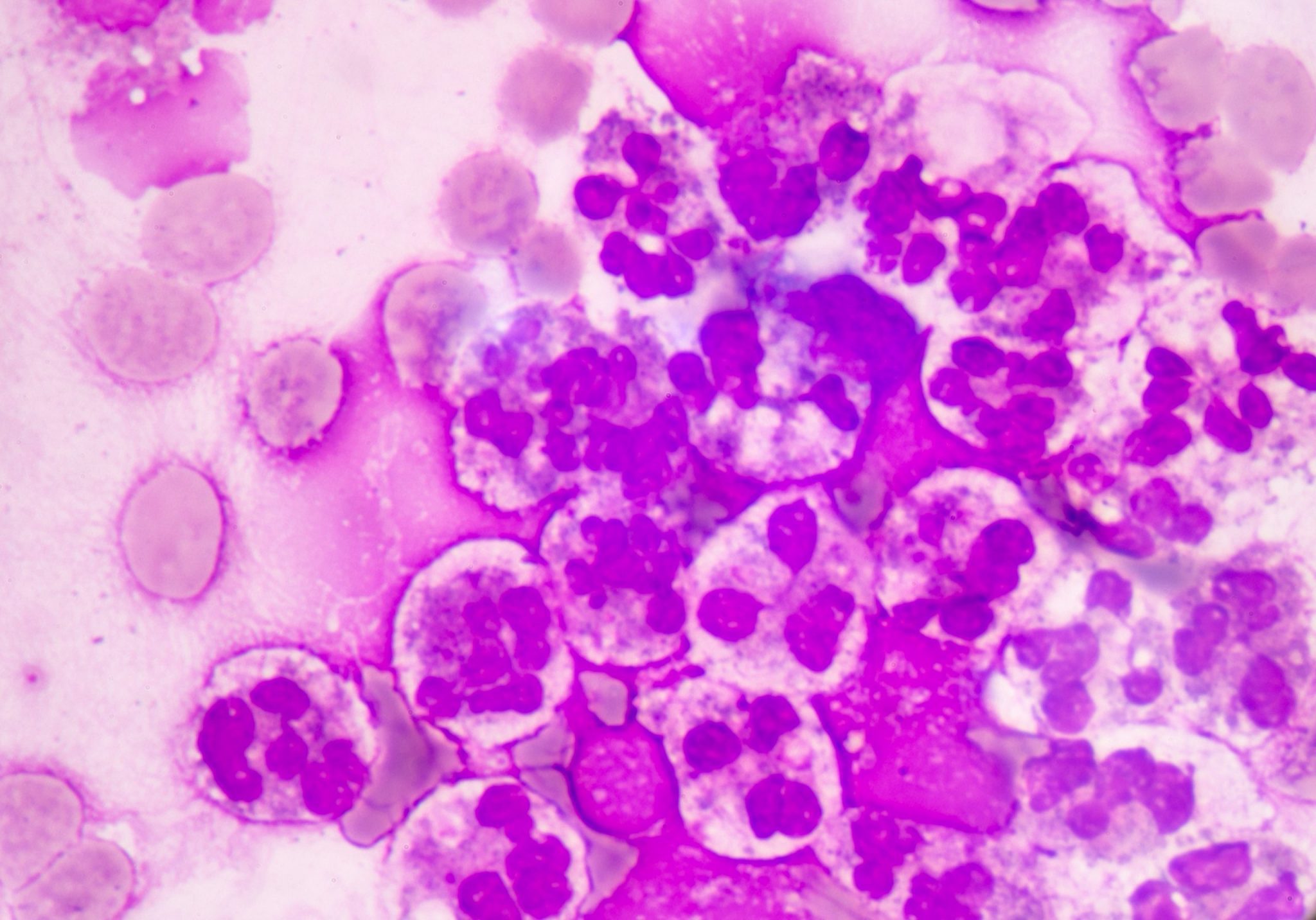
The study of these liquids is considered an indispensable tool in the delivery of assertive data for the diagnosis.
Cavitary liquids analysis is extremely important to provide essential data for the diagnosis, effective therapeutic process and monitoring of pathological conditions, such as complications from chronic liver and heart diseases, as well as tuberculosis and synovitis, among several others.
In recent years, there has been a greater interest in the development of automated analysis of body fluids, mainly due to the limitations of manual cell counting, caused by the lack of experience of the observer or the lack of standardization of the analysis process itself.
Nowadays, several devices have a specific module for the analysis of biological fluids, providing good correlations between manual and automated methods. Specifically for the total counts of nucleated cells (TC-BF) and white blood cells (WBC-BF) in cavitary liquids, according to observations in articles. However, it is worth mentioning that cell differentiation should always be performed using manual light microscopy.
This evolutionary scenario of automation in correlation with manual methods optimizes exam processes, both in terms of time and reproducibility of the analyses. In other words, it allows for a shorter release time and greater reliability of the results.
Cavitary Liquids Processes Control
Faced with the application of manual optical microscopy in the routine, some variables impact the result of the analysis of cavitary liquids, such as: the lack of experience of the observer, the use of inappropriate inputs and the lack of standardization of the process. Aiming at an adequate performance in the analysis of liquids, each laboratory defines its process flow based on the chosen accreditation standards, in order to obtain a good control and consequently a reliable result. In these flows, it is recommended that the cellular analysis of cavitary liquids be performed in the Fuchs Rosenthal chamber, according to Prof. Guilherme Dienstmann, Biomedical and Scientific Advisor at Controllab. The performance of the slide for cytomorphological analysis, when in the presence of low cellularity, should be performed after using a cytocentrifuge and with a Romanowski-derived dye. Additionally, continuous training must be performed with the laboratory professionals, seeking the evolution and optimization of the processes. For an excellent laboratory analysis, the resources provided must be observed, which includes evaluating the need to acquire new inputs and more modern equipment as an investment for this recognition. For professional updating, scientific article platforms such as Scielo and PubMed can be valuable reference sources. Guidance provided by quality control providers and accreditation standards also complement these sources.Quality Control in Cavitary Liquids
Quality control must follow the constant evolution of analytical routines. It is possible to identify companies that supply equipment with a specific module for biological liquids together with the commercial control for this module. When the commercial control is produced by a supplier other than the equipment manufacturer, it is possible to detect more sensitive variations, which would not be detected when using the control developed specifically for a given analytical system. These controls produced by manufacturers other than the analytical system itself are known as third opinion controls. These are independent controls, which generally include inter-laboratory assessment in different systems and reliably reproduce the performance of patient samples, providing an unbiased evaluation. It is also possible that the laboratory itself produces its controls, provided that the chosen accreditation standards are observed. Applying continuous monitoring (known as Internal Control) and periodic external comparison (known as External Control or Proficiency Testing) builds reliability into analytical routines. The application of Internal Control helps the laboratory to identify random errors that may interfere with the analysis results. When the laboratory participates in the External Control, it is able to identify whether there is an incidence of positive and negative trends occurring in its routine (systematic errors). Controllab is a laboratory quality control provider with 45 years of experience. It has a qualified technical team advised by specialists in the control areas offered. The statistical analyzes and control of the samples used in the services are rigorously evaluated by these professionals. Among the controls offered by Controllab, the solutions offered for the Cavitary Liquids routines stand out. The comprehensive program includes both automated and manual methodologies. Check out Controllab’s Cavitary Liquids programs:|
Programs |
Tests covered |
Available services |
|
| Multiparameters | Biochemistry |
Lactic Acid (Lactate), Uric Acid, Adenosine Deaminase (ADA), Albumin, Amylase, Total Bilirubin, Total Calcium, Chlorides, Cholesterol, Creatinine, Density, Lactic Dehydrogenase (LDH), Ferritin, Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP), GT Gamma, Glucose, Lipase, pH, Potassium, Total Proteins, Sodium, Triglycerides and Urea |
  |
| Immunology |
Alpha-1-Acid Glycoprotein, CA 125, CA 15-3, CA 19-9, CEA, Complement C3 and C4 |
||
| Cell Count |
Nucleated Cells and Red Cells, Cell Identification and Cytology |
||
| Automated Cell Counting |
Nucleated Cells and RBCs |
  |
|
| Synovial Fluid: Crystals |
Crystal Identification |
 |
|