Background - Aim
HIV infection remains a critical global public health issue, affecting approximately 38 million individuals worldwide, with a significant burden in sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia. Antibody-based rapid and point-of-care tests (POCT) for HIV (anti-HIV) are key tools in expanding access to diagnostics, particularly in resource-limited settings. External Quality Assessment Programs (EQAP) are essential to ensure these diagnostic methods’ accuracy, reliability, and harmonization. This study aims to assess the diagnostic proficiency of laboratories participating in an EQAP for anti-HIV POCT, which was conducted by a Brazilian provider accredited to ABNT NBR ISO/IEC 17043:2011.
Methods
Data from 2010 to 2024 were analyzed, encompassing four annual rounds. Participants tested four lyophilized and/or liquid quality control samples per round. The metrics evaluated included the number of participants, testing methods, adequacy rates (%A), specificity (SP), and sensitivity (SE).
Results
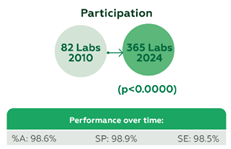
928 laboratories contributed 58,409 datasets, including 903 from Brazil and 25 from Bolivia, Colombia, and Panama. Laboratory participation increased significantly, from 82 in 2010 to 365 in 2024 (p=0.0000), and consolidated in more than 300 since 2021. Performance metrics were consistently high, with an overall %A of 98.6%, SP of 98.9%, and SE of 98.5% (Figure 1). Immunochromatography was the predominant testing method, achieving %A 98.7%, SP 98.9%, SE 98.5%, 99% true-negative results, and 98.1% true-positive results. Performance by the most commonly used kits was as follows:
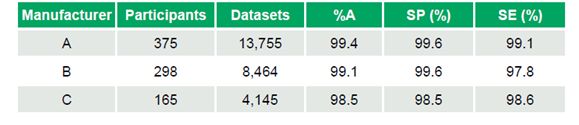
- Manufacturer A: 375 participants, 13,755 datasets, %A 99.4%, SP 99.6%, SE 99.1%
- Manufacturer B: 298 participants, 8,464 datasets, %A 99.1%, SP 99.6%, SE 97.8%
- Manufacturer C: 165 participants, 4,145 datasets, %A 98.5%, SP 98.5%, SE 98.6%
Conclusions
This study demonstrates the growing adoption of anti-HIV POCT in Brazil and neighboring countries, as evidenced by significant increases in EQAP enrollment and consistently high-performance metrics. These findings underscore the reliability and effectiveness of anti-HIV POCT detection and highlight the pivotal role of EQAPs in maintaining diagnostic accuracy and advancing quality standards across the region.
References
Di Germanio C, Yufenyuy EL, Hampton DC, Thorbrogger C, Parekh BS, Norris PJ. A Stable Dried Tube Specimen for Quality Assurance and Training Programs for HIV Rapid Test for Recent Infection. Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1): e0339822. doi:10.1128/spectrum.03398-22. Epub 2023 Jan17. PMID:36648237; PMCID: PMC9927143.
Smallwood M, Vijh R, Nauche B, Lebouché B, Joseph L, Pant Pai N. Evaluation of a Rapid Point of Care Test for Detecting Acute and Established HIV Infection, and Examining the Role of Study Quality on Diagnostic Accuracy: A Bayesian MetaAnalysis. PLoS One. 2016 Feb18;11(2): e0149592. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone. 0149592. PMID:26891218; PMCID: PMC4758636.